

Uganda’s infrastructure sector is critical to its long-term economic growth and sustainable development. As the country urbanizes and expands its economy, the demand for improved transportation, energy, water supply, and ICT infrastructure is rapidly increasing. With a strong emphasis on public infrastructure development, Uganda is prioritizing large-scale projects to boost trade, enhance connectivity, and facilitate industrial growth.
Investors have a unique opportunity to be part of Uganda’s ambitious infrastructure agenda, which includes modernizing transport networks, expanding energy capacity, upgrading digital infrastructure, and improving urban services. Strategic investments in this sector are crucial for supporting other industries, such as agriculture, manufacturing, and tourism, while ensuring Uganda remains competitive in the regional and global economy.
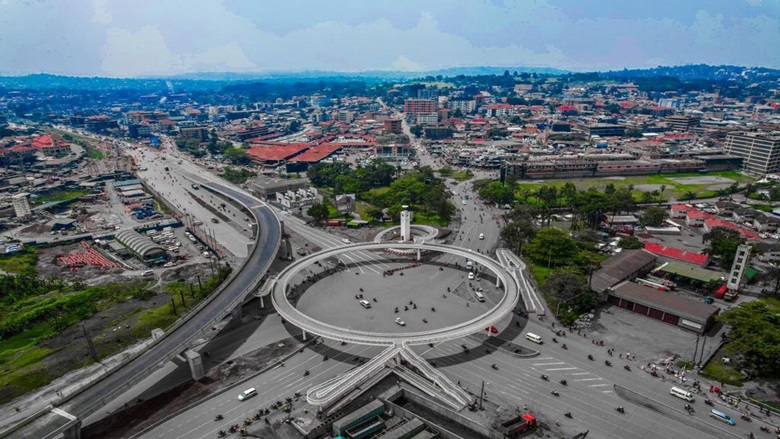

Uganda’s road transport sector presents key investment opportunities as the country expands and upgrades its road network. Investors can contribute to improving highways, developing urban transport systems, and enhancing regional trade routes, which are essential for boosting economic growth and reducing congestion.
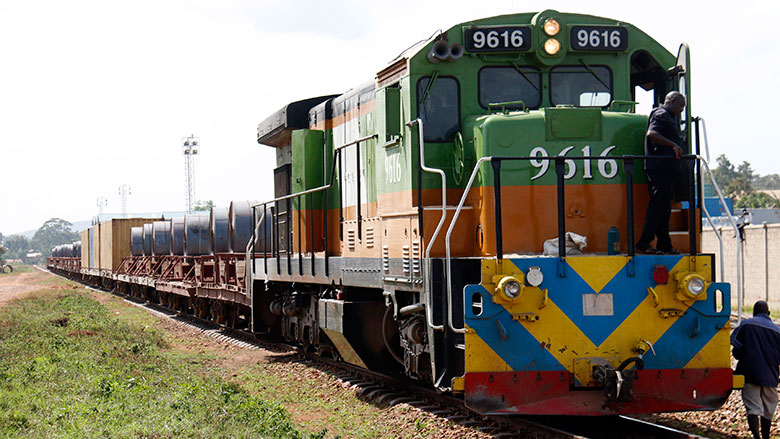
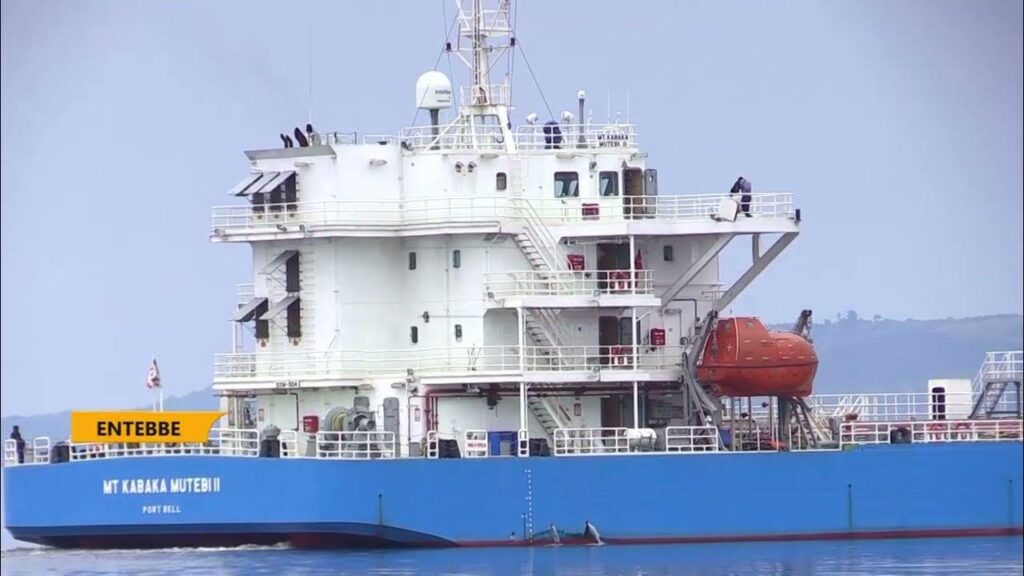


Uganda’s lakes and rivers offer great potential for water transport investment, with opportunities in cargo and passenger services, tourism, and port infrastructure. Investors can benefit from government incentives and help boost trade, reduce road congestion, and support regional connectivity.
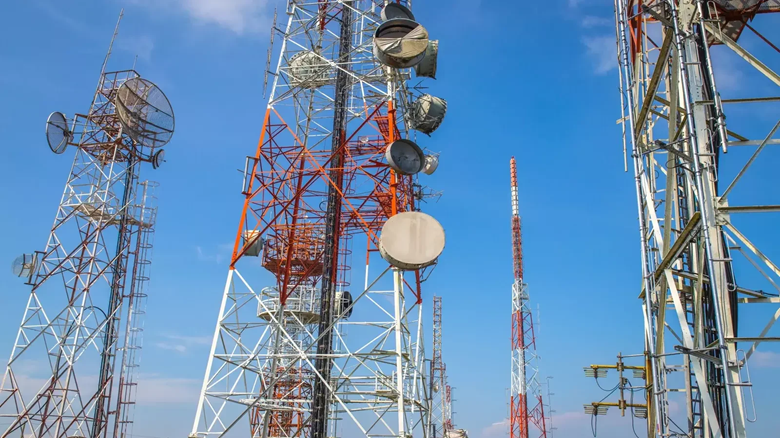

With the growing reliance on digital technologies, Uganda’s ICT infrastructure presents significant investment opportunities. Investors can contribute to expanding internet connectivity, building data centers, and enhancing digital services,
Government Commitment to Infrastructure Development
Uganda’s government has placed infrastructure at the heart of its national development strategy, prioritizing projects in transport, energy, and urban services to support economic growth.
Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs)
The government has embraced Public-Private Partnerships to execute large infrastructure projects, providing investors with a platform to collaborate on projects such as highways, airports, and energy plants. This approach offers lucrative opportunities for private sector involvement.
Strategic Location for Regional Trade
Uganda is positioned as a key trade hub within the East African Community (EAC), providing investors access to markets in neighboring countries. Infrastructure investments in transportation and logistics can tap into regional trade and commerce.
Expanding Energy Sector
The demand for energy in Uganda is growing as industries expand and urbanization increases. With potential for hydro, solar, and renewable energy sources, investors can explore opportunities in energy production and distribution to meet the rising demand.
Rapid Urbanization
Uganda’s urban centers are growing quickly, leading to a demand for better roads, housing, water supply, waste management, and public transportation. Infrastructure projects aimed at improving urban living conditions present attractive investment prospects.
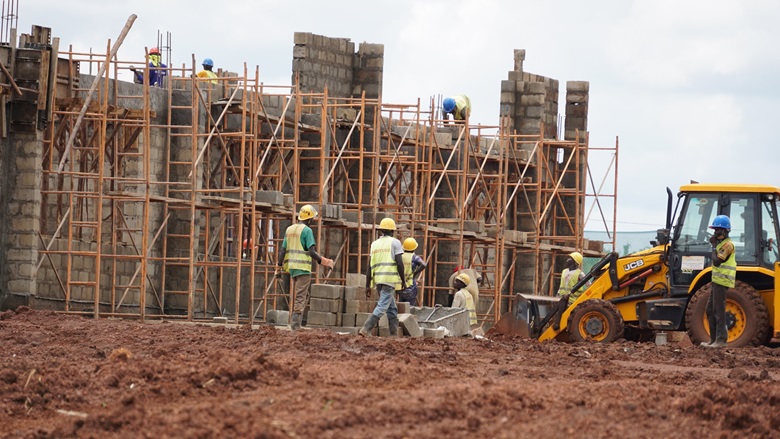

Uganda’s fast-growing urban population demands modern housing and improved urban services to meet the needs of its residents. This presents a compelling opportunity for investors to engage in various projects aimed at enhancing the urban landscape. They can participate in the development of public housing projects that provide affordable living spaces, the construction of smart cities equipped with advanced technology for better resource management, and the establishment of modern urban utilities, such as efficient public transport systems and effective waste management solutions.
